Health insurance in Germany
Germany is an attractive destination for expats due to its strong economy, high standard of living, and diverse cultural offerings. However, as an expat in Germany, it’s important to consider your healthcare needs and options. While Germany has a world-class healthcare system, it can be expensive for those without health insurance.
This is where health insurance for expats comes in – it provides a safety net for unexpected medical expenses and ensures that you have access to the best possible healthcare.
In this article, we will explore the importance of health insurance for expats in Germany, what types there are, how the system works and which is right for you.
Importance of health insurance
Why do you need health insurance as an expat in Germany, and what are the main reasons?
There are several reasons why health insurance is crucial for expats living in Germany. Here are some of the most important ones:
Access to healthcare
Germany has one of the best healthcare systems in the world, but it can be expensive for those without health insurance. Without insurance, you may not be able to access the same level of care that you would with insurance.
Legal requirement
Health insurance is mandatory in Germany for all residents, including expats. Failure to have adequate insurance can result in fines or even deportation.
Protection from high medical costs
Healthcare costs in Germany can be high, especially for emergency care or specialized treatment. With insurance, you’ll be protected from these costs and won’t have to worry about paying large medical bills out of pocket.
Peace of mind
Knowing that you have comprehensive health insurance coverage can give you peace of mind and allow you to focus on other aspects of your life in Germany, without worrying about your healthcare needs.
Better job prospects
Many employers in Germany require their employees to have health insurance, so having coverage can increase your job prospects and make you a more desirable candidate.
So, why do you need health insurance as an expat?
Overall, health insurance is a critical aspect of life in Germany for expats. It ensures that you have access to quality healthcare, protects you from high medical costs, and is a legal requirement for all residents.
What are the consequences of not having health insurance?
Not having health insurance as an expat in Germany can have serious consequences. Here are some of the main ones:
Legal issues
Health insurance is mandatory for all residents in Germany, including expats. If you do not have health insurance, you may face legal issues, including fines, deportation, or even imprisonment in extreme cases.
Limited access to healthcare
Without health insurance, you may not be able to access the same level of healthcare as those with insurance. You may be limited to emergency care only, and may not have access to specialized treatment or non-emergency procedures.
Financial burden
Healthcare costs in Germany can be high, especially for emergency care or specialized treatment. Without insurance, you’ll be responsible for paying these costs out of pocket, which can be a significant financial burden.
Limited job prospects
Many employers in Germany require their employees to have health insurance. If you do not have insurance, you may be limited in your job prospects and may have difficulty finding employment.
Risk to health
Without insurance, you may be reluctant to seek medical treatment when you need it, which can lead to serious health risks. Delaying treatment or not receiving proper care can result in more severe health problems in the long run.
Summary: Why do you need health insurance in Germany?
Overall, not having health insurance as an expat in Germany can have serious consequences, including legal issues, limited access to healthcare, financial burden, limited job prospects, and risks to your health.
It’s essential to have adequate health insurance coverage to protect yourself and ensure that you have access to the best possible healthcare.
How does the health insurance system in Germany work? The two types of health insurance

There are two types of health insurance in Germany – statutory and private health insurance. To understand how both work and what the key differences are, you need to look at the following key topics which we will expand upon. They are:
- Enrollment/eligibility
- Contributions/cost
- Coverage
- Co-payments
- Choice of doctors
- Additional coverage/switching health insurance types
Statutory health insurance
The statutory health insurance system in Germany is a government-regulated insurance program that provides healthcare coverage to the majority of the population, including employees, students, and low-income earners. Here’s how it works:
1. Statutory health insurance: Enrollment
Employees with a gross salary of up to €66,600 per year are required to enroll in statutory health insurance. Students, self-employed individuals, and low-income earners may also be eligible for statutory health insurance.
2. Statutory health insurance: Contributions
The cost of statutory health insurance is split between the employee and the employer, with each contributing approximately 7.3% of the employee’s gross salary. Self-employed individuals and students pay a fixed monthly fee based on their income.
3. Statutory health insurance: Coverage
Statutory health insurance covers a wide range of medical services, including doctor’s visits, hospital stays, prescription medication, and some dental procedures.
4. Statutory health insurance: Co-payments
Patients may be required to make co-payments for some medical services, such as prescription medication or hospital stays. The amount of the co-payment varies depending on the service and the health insurance provider.
5. Statutory health insurance: Choice of doctors
Patients with statutory health insurance can choose their own doctor, although some specialists may require a referral from a general practitioner.
6. Statutory health insurance: Additional coverage
Patients may choose to purchase additional private health insurance to cover services not covered by statutory health insurance or to receive access to private hospitals or doctors.
Statutory health insurance in Germany provides comprehensive healthcare coverage to the majority of the population at an affordable cost. While there are some limitations and co-payments, patients have the freedom to choose their own doctors and receive a high standard of care.
Private health insurance
Private health insurance (PHI) in Germany is an alternative to the statutory health insurance system and is primarily available to high-income earners and self-employed individuals.
Using the 6 steps as discussed in the introduction of this section, using the statutory health insurance as a comparison, here’s an overview of how the system works:
1. Private health insurance: Eligibility
Individuals who earn more than €66,600 per year or are self-employed can opt for private health insurance. Students and employees with low incomes may also be eligible for private health insurance, but they must meet certain criteria.
2. Private health insurance: Cost
The cost of private health insurance varies depending on the individual’s age, health status, and coverage needs. Premiums are generally higher than statutory health insurance, but they can provide additional benefits and more flexibility.
3. Private health insurance: Coverage
Private health insurance plans offer more extensive coverage than statutory health insurance, including access to private hospitals and doctors, alternative medicine, and specialized treatments.
4. Private health insurance: Co-payments
Patients with private health insurance may still be required to make co-payments for some medical services, although the amount is generally lower than in the statutory system.
5. Private health insurance: Choice of doctors
Patients with private health insurance can choose their own doctors and may have access to a wider range of specialists.
6. Private health insurance: Switching back to statutory health insurance
Once an individual has opted for private health insurance, it can be difficult to switch back to the statutory system. They may be required to undergo a health examination and could be subject to waiting periods for certain treatments.
Overall, private health insurance in Germany offers additional benefits and flexibility for high-income earners and self-employed individuals.
However, it can be more expensive than the statutory system and may not be suitable for everyone. It’s important to carefully consider your coverage needs and consult with an insurance provider before making a decision.
What are the key differences between statutory and private health insurance in Germany?

Drawing upon the 6 key themes as mentioned above, the key differences between statutory and private health insurance are:
Difference 1: Eligibility
Statutory health insurance is mandatory for employees with a gross salary of up to €66,600 per year, while private health insurance is primarily available to high-income earners and self-employed individuals.
Difference 2: Cost
The cost of statutory health insurance is split between the employee and the employer, while private health insurance premiums are generally paid solely by the individual. Private health insurance premiums can be higher than statutory health insurance premiums, but they may provide additional benefits and more flexibility.
Difference 3: Coverage
Statutory health insurance provides basic healthcare coverage, including doctor’s visits, hospital stays, and prescription medication. Private health insurance plans offer more extensive coverage, including access to private hospitals and doctors, alternative medicine, and specialised treatments.
Difference 4: Co-payments
Patients with statutory health insurance may be required to make co-payments for some medical services, while patients with private health insurance may also be required to make co-payments, although the amount is generally lower.
Difference 5: Choice of doctors
Patients with statutory health insurance can choose their own doctors, although some specialists may require a referral from a general practitioner. Patients with private health insurance can choose their own doctors and may have access to a wider range of specialists.
Difference 6: Switching back to statutory health insurance
Once an individual has opted for private health insurance, it can be difficult to switch back to the statutory system. They may be required to undergo a health examination and could be subject to waiting periods for certain treatments.
What insurance provider should I go for?
Find out which statutory or private health insurance provider best covers your needs.
What additional insurances to the statutory health insurance might expats in Germany need?
When you’re publicly insured in Germany, only your essential health needs are covered. However, you may want to consider increasing the basic coverage of your statutory insurance by opting for additional supplementary coverage.
Additional insurance 1: Travel insurance
Expats who travel frequently outside of Germany may want to consider international health insurance to ensure they are covered while abroad.
Additional insurance 2: Dental insurance
Dental services are not fully covered by statutory health insurance in Germany, so expats may want to consider purchasing dental insurance to cover routine check-ups, cleanings, and more extensive dental procedures.
Additional health insurance: A summary
Overall, the additional health insurance needs of expats in Germany will depend on individual circumstances and coverage needs. It’s important to carefully consider the options and consult with an insurance provider to ensure that you have the coverage you need.
Information for expats: What you need to know about health insurance in Germany
If you’re an expat living in Germany, here are some important things you need to know about health insurance:
Health insurance is mandatory
All residents of Germany are required to have health insurance, either through the statutory health insurance system or through private health insurance.
Statutory health insurance is mandatory for most employees
Employees with a gross salary of up to €66,600 per year are required to have statutory health insurance. The cost of statutory health insurance is split between the employee and the employer.
Private health insurance is available for high-income earners and self-employed individuals
If you earn more than €66,600 per year or are self-employed, you can opt for private health insurance.
Coverage may vary
The coverage provided by statutory and private health insurance may vary, so it’s important to carefully consider your coverage needs when choosing a plan.
Additional health insurance may be necessary
Expats in Germany may want to consider purchasing additional health insurance to supplement their statutory or private health insurance, such as international health insurance, dental insurance, and personal liability insurance.
Switching between health insurance plans can be difficult
Once you have chosen a health insurance plan, switching to a different plan can be difficult and may require a health examination or waiting period.
Healthcare in Germany is generally of high quality
Germany has a high-quality healthcare system, with modern facilities and well-trained medical professionals.
What documents do expats need to apply for health insurance in Germany?
The required documents for applying for health insurance in Germany can vary depending on whether you are applying for statutory health insurance or private health insurance.
We’ve put together this checklist of the general documents you’ll need:
Passport
You will need a valid passport to prove your identity.
Residence permit
If you are a non-EU citizen, you will need a valid residence permit to prove your right to reside in Germany.
Proof of income
If you are applying for statutory health insurance, you will need to provide proof of income, such as pay slips or tax returns. If you are self-employed, you may need to provide additional documents such as a business registration certificate or proof of income.
Registration (Anmeldung)
You will need to provide proof of your registration with the local authorities (Anmeldung).
Health certificate
Some insurance providers may require a health certificate or medical examination to determine your eligibility for coverage.
Previous insurance documentation
If you have had previous health insurance coverage, you may need to provide documentation to prove your coverage history.
Bank account information
You will need to provide your bank account information for the payment of insurance premiums.
Benefits and drawbacks of statutory and private health insurance

In this section, we’ll take a look at the benefits and drawbacks of both statutory and private health insurance for expats in Germany.
Benefits of and drawbacks statutory health insurance for expats
There are many benefits and drawbacks of statutory health insurance expats in Germany should consider, depending on their situation.
Benefits of statutory health insurance
Benefits include:
Benefit 1: Comprehensive coverage
Statutory health insurance provides comprehensive coverage for a wide range of healthcare services, including doctor visits, hospital stays, and prescription medications.
Benefit 2: Affordable premiums
The cost of statutory health insurance is split between the employee and the employer, and the premiums are generally lower than private health insurance premiums.
Benefit 3: No medical exams
Most people are automatically accepted into statutory health insurance without the need for a medical exam.
Benefit 4: Family coverage
Spouses and children can be included in the coverage at no additional cost.
Benefit 5: No exclusion for pre-existing conditions
Unlike private health insurance, statutory health insurance cannot exclude coverage for pre-existing conditions.
Benefit 6: High quality of care
The German healthcare system is known for its high quality of care, and statutory health insurance plans provide access to this care.
Benefit 7: Access to specialists
Statutory health insurance provides access to specialists without needing a referral from a general practitioner.
Benefit 8: Easy to navigate
The German healthcare system is well-organised and easy to navigate, making it easy for expats to understand and access their healthcare benefits.
Drawbacks of statutory health insurance for expats
Drawbacks of the statutory health insurance for expats include:
Drawback 1: Limited flexibility
Statutory health insurance plans offer limited flexibility in terms of coverage options and provider choices compared to private health insurance plans.
Drawback 2: Income-dependent premiums
The premiums for statutory health insurance are income-dependent, so high earners may pay more for coverage than they would with private health insurance.
Drawback 3: Limited access to English-speaking doctors
While most doctors in Germany speak English, expats may have difficulty finding doctors who are fluent in English in some areas of the country.
Drawback 4: Limited coverage for alternative medicine
Statutory health insurance may not provide coverage for alternative medicine treatments like acupuncture, chiropractic care, or naturopathy.
Drawback 5: Long waiting times for non-emergency procedures
Although there are generally no waiting periods for medical treatments or procedures under statutory health insurance, non-emergency procedures may have long wait times.
Drawback 6: No personalised coverage
Statutory health insurance plans do not offer personalized coverage options based on individual needs like some private health insurance plans.
Statutory health insurance
Pros
- Comprehensive cover
- Affordable premiums
- No medical entry exams
- Family coverage
- No exclusion for pre-existing conditions
- High quality care
- Access to specialists
- Easy to navigate
Cons
- Limited flexibility
- Income-dependent premiums
- Limited access to English speaking doctors
- Limited coverage for alternative medicine
- Long waiting times for non-emergency procedures
- No personalised coverage
What statutory health insurance provider is right for me?
Compare statutory health insurance providers on our comparison tool.
Benefits and drawbacks of private health insurance for expats
As with the statutory health insurance, the private health insurance has various benefits for expats, depending on their situation.
Benefits of private health insurance
Here are some of the benefits of private health insurance for expats in Germany:
Benefit 1: More comprehensive coverage
Private health insurance plans often offer more comprehensive coverage than statutory health insurance, including coverage for alternative medicine, dental care, and vision care.
Benefit 2: Greater flexibility
Private health insurance plans offer greater flexibility in terms of coverage options, provider choices, and waiting times for non-emergency procedures.
Benefit 3: Personalised coverage
Private health insurance plans often offer personalized coverage options based on individual needs and preferences.
Benefit 4: Access to English-speaking doctors
Private health insurance plans may offer access to English-speaking doctors or provide translation services for medical appointments.
Benefit 5: Shorter waiting times
Private health insurance plans may offer shorter waiting times for non-emergency procedures.
Benefit 6: Higher quality care
Some private health insurance plans offer access to exclusive healthcare facilities or specialised treatments that may not be available under statutory health insurance.
Benefit 7: No income-dependent premiums
Private health insurance premiums are not income-dependent, so high earners may pay less for coverage than they would with statutory health insurance.
Drawbacks of private health insurance for expats
If you are considering taking out private health insurance, however, you should be aware of the drawbacks. These are:
Drawback 1: Higher premiums
Private health insurance plans often have higher premiums than statutory health insurance plans, which may make it difficult for some expats to afford.
Drawback 2: Limited acceptance
Not all healthcare providers in Germany accept private health insurance, which may limit the choices of healthcare providers for expats.
Drawback 3: Medical exams and exclusions
Private health insurance plans may require a medical exam or exclude coverage for pre-existing conditions, which could be problematic for some expats.
Drawback 4: Limited family coverage
Private health insurance plans may charge extra for family coverage or limit the number of dependents that can be covered.
Drawback 5: Language barriers
Some private health insurance plans may not offer language services or access to English-speaking doctors, which could be a problem for expats who do not speak German fluently.
Drawback 6: Bureaucratic hurdles
Private health insurance plans may require more paperwork and administrative work than statutory health insurance, which could be a hassle for some expats.
Private health insurance
Pros
- More comprehensive coverage
- Greater flexibility
- Personalised coverage
- Access to English-speaking doctors
- Shorter waiting times
- Higher quality care
- No income-dependent premiums
Cons
- Higher premiums
- Limited acceptance
- Medical exams and exclusions
- Limited family coverage
- Language barriers
- Bureaucratic hurdles
Which private health insurance provider is best for me?
Compare various plans offered by private providers based on your needs.
So, what type of health insurance is right for expats?

There are a number of factors expats should consider when choosing a health insurance type in Germany. Ultimately, these factors may differ in importance for the individual when opting for a health insurance type. These factors are:
Factor 1: Coverage
Expats should consider the level of coverage that they need based on their personal health needs and preferences.
Factor 2: Cost
Expats should consider the cost of health insurance premiums and any additional fees, such as deductibles and co-pays.
Factor 3: Provider network
Expats should consider whether the health insurance plan has a network of healthcare providers that meet their needs, including English-speaking doctors or providers who specialize in specific medical treatments.
Factor 4: Waiting times
Expats should consider the waiting times for medical procedures and treatments under the health insurance plan.
Factor 5: Flexibility
Expats should consider whether the health insurance plan offers flexibility in terms of coverage options and provider choices.
Factor 6: Exclusions
Expats should review any exclusions or limitations in the health insurance plan, including coverage for pre-existing conditions or specific medical treatments.
Factor 7: Administrative requirements
Expats should consider the administrative requirements of the health insurance plan, including paperwork and communication in German.
Factor 8: Personal situation
Expats should consider their personal situation, including family status and income level when choosing a health insurance plan.
What type of health insurance is right for me? Flowchart
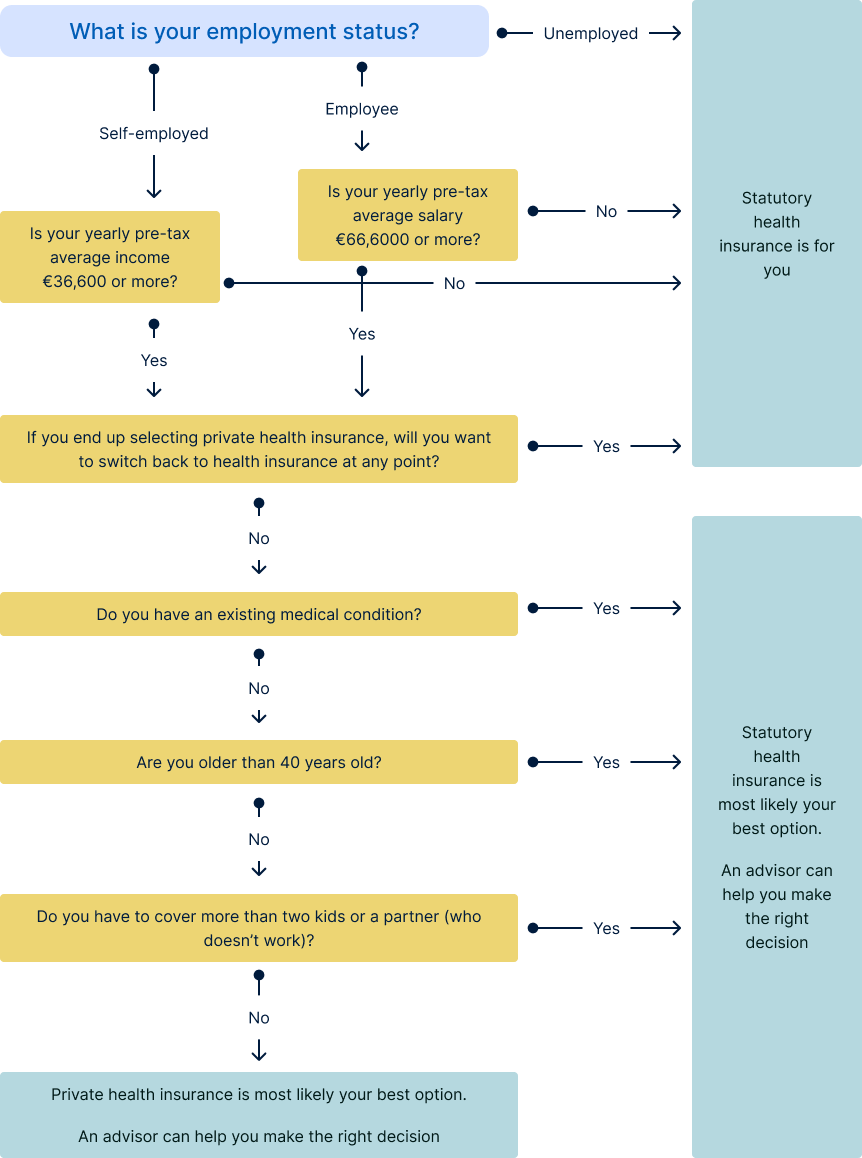
Not sure which type of health insurance is right for you? This flowchart can help you out.
Health insurance for expats in Germany: A summary
As discussed in the article, expats in Germany are required to have health insurance, which can be either public or private. Public insurance is mandatory for those earning less than a certain income threshold, while private insurance is an option for those who meet certain criteria.
All in all, the German healthcare system is highly regulated and provides quality medical care.
Unsure which health insurance provider to pick?
Compare health insurance providers on our comparison tool.


